Dentures
Removable Prosthodontics
A denture is a removable replacement for missing teeth and surrounding tissues. Two types of dentures are available -- complete and partial dentures. Complete dentures are used when all the teeth are missing, while partial dentures are used when some natural teeth remain.
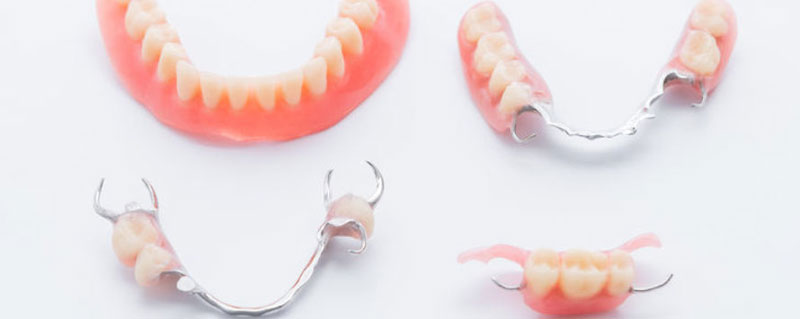
Complete Dentures
Complete dentures can be either "conventional" or "immediate." Made after the teeth have been removed and the gum tissue has begun to heal, a conventional denture is ready for placement in the mouth about eight to 12 weeks after the teeth have been removed.
Unlike conventional dentures, immediate dentures are made in advance and can be positioned as soon as the teeth are removed. As a result, the wearer does not have to be without teeth during the healing period. However, bones and gums shrink over time, especially during the healing period following tooth removal. Therefore a disadvantage of immediate dentures compared with conventional dentures is that they require more adjustments to fit properly during the healing process and generally should only be considered a temporary solution until conventional dentures can be made.
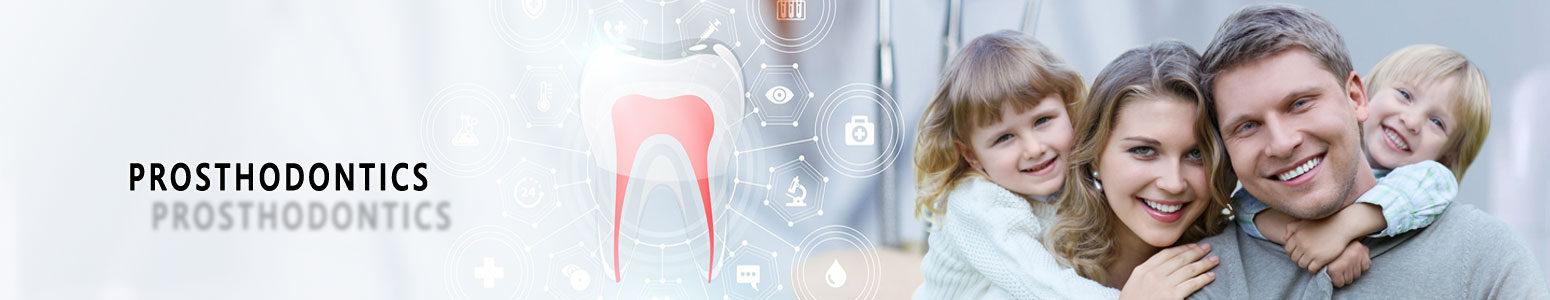
Partial Dentures
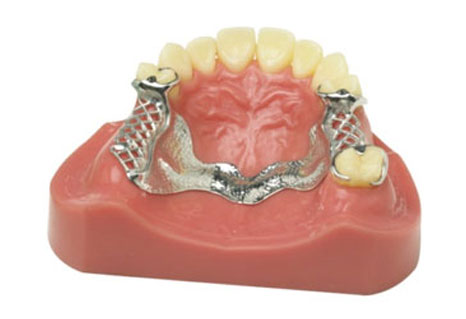
A removable partial denture usually consists of replacement teeth attached to a pink or gum-colored plastic base, that holds the denture in place in the mouth. Partial dentures are used when one or more natural teeth remain in the upper or lower jaw. Not only does a partial denture fill in the spaces created by missing teeth, it prevents other teeth from changing position.

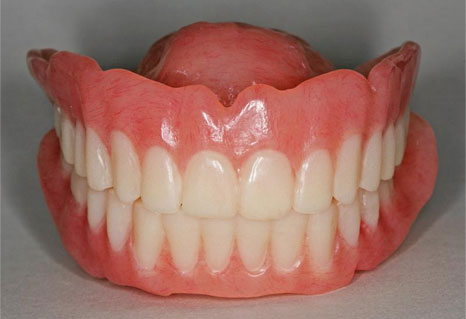
Implant retained dentures
If the patient has NO teeth at all in any given arch (upper or lower), a full mouth of individual implants attached to porcelain teeth and bridges could cost about what an expensive automobile costs.
On the other hand, a minimum of 2 implants can maintain a lower denture which would not otherwise be tolerated by that patient. More than two implants are needed for upper implant retained dentures.
Implant retained dentures have special significance for people who cannot wear lower dentures. As an edentulous (toothless) person ages, and the bone continues to resorb away, lower ridges frequently disappear entirely. Thus there is no vertical bone underlying the gums to stabilize a lower denture. These people frequently cannot wear a lower denture at all. The addition of two implants in the front of the lower jaw can make it possible to retain a lower denture which would otherwise be impossible for the patient to tolerate.
Cast Partial Dentures
A partial denture may be tooth-supported or tooth and tissue-supported. There are significant differences between these two types of dentures.
The number of teeth remaining, the position and the stability of the teeth are only a few of the factors that help to determine what style or type of partial denture would be best for you.
Partials can be made of different materials, including acrylics, a metal/acrylic combination or flexible thermoplastics.
Acrylic partials are usually used as a transitional or temporary replacement of missing teeth, depending on your personal circumstances.
The metal/acrylic partial - commonly called a cast partial - is usually a more rigid and permanent style of denture. The metal is either a highly compatible chrome cobalt alloy or titanium, which are both ultra thin, light and very strong.
Valplast/Flexible Dentures
The new flexible thermoplastics have the advantage of aesthetics and flexibility. All partials are designed to be removable and should be removed nightly to contribute to a healthy oral environment.